Rwanda
Since the 1994 genocide and collapse of the economy, Rwanda has made significant improvements in poverty reduction and quality of life. But the effects of climate change on food and agriculture are threatening those advances.
WFP/Fredrik Lerneryd
Make a difference in Rwanda
Hunger Stats
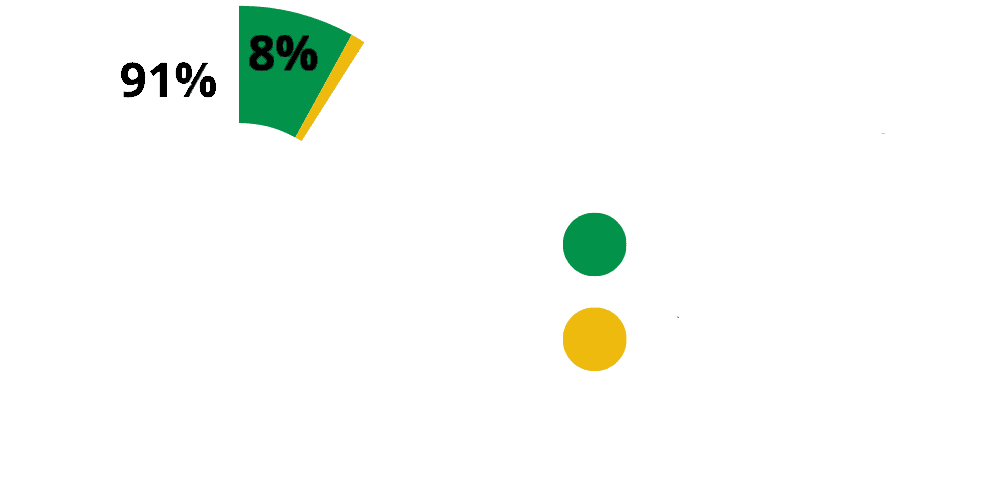
With many 69% of rural households dependent on small-scale farming, irregular climate is making food insecurity a growing problem.
1/5
of people are food insecure
32%
of children under 5 are malnourished
38%
of Rwandans live in poverty
1/5
of people are food insecure
32%
of children under 5 are malnourished
38%
of Rwandans live in poverty
1/5
of people are food insecure
Rwanda Facts
New York
Show Places

New York
×
Geocoding Error Occured.
Tried to Geocode: Rwanda
Error Type: ERROR
Please be sure to follow the tutorial on how to setup the Google APIs required for the Advanced Google Map Widget.
Google Map API Key Tutorial
Population: 13.2 million people.
Background: Rwanda gained its independence in 1962. Since the 1994 genocide, its made steady economic and social progress.
Geography & Climate: Rwanda is a landlocked country in central Africa, bordered by Uganda, Tanzania, Burundi and the Democratic Republic of Congo. It is hilly and mountainous with a tropical climate.
Economy: Rwanda’s economy is largely agricultural, with most people relying on small-scale farming for food and income.
Causes of Hunger
Irregular Climate
Rwanda faces climate vulnerabilities including land degradation, floods, landslides and droughts, undermining food and nutrition security. Degrading soils and climate change affect the country’s agricultural production.
Learn More Rural Poverty
Rwanda was listed among the top ten countries worldwide with the highest food inflation rates in 2023, jeopardizing food and nutrition security, straining livelihoods and impeding Rwandans’ already poor purchasing power.
Learn More Host to Refugees
In 2023, Rwanda hosted 135,000 refugees and asylum seekers mostly from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and Burundi, with 90% residing in camps and transit sites. Livelihood opportunities for camp-based refugees continue to be neglected by the lack of land for farming and raising livestock, and the lack of livelihood funding. Given the escalation of violence in the DRC, Rwanda can expect an increase in people fleeing into the country to seek refuge.
Learn More  WFP/John Paul Sesonga
WFP/John Paul SesongaWFP’s Hunger Relief
Present in Rwanda since 1975, WFP’s main priority is to provide food assistance to refugees, safety net assistance to the most vulnerable, and build national capacity to design and manage home-grown hunger solutions.

Food Assistance
When disasters strike, we provide people with immediate food and nutrition assistance. WFP provides targeted cash-based transfers to over 127,000 refugees in five camps, so they can buy food of their choice. Rwandan refugees returning home are also supported, to help them re-integrate into their communities.

School Meals
Nutritious school meals are provided to 117,000 pre-primary and primary students across 140 institutions in the country. WFP and its partners also implement complementary activities at the supported schools to enhance education outcomes among the targeted students.

Small-Scale Farming
WFP works to help small-scale farmers, especially women, have increased supplies and access to markets. This includes strengthening small-scale farmer cooperatives, improving access to finance and predictable markets and implementing initiatives to reduce post-harvest losses.
Lastest News
- Blog
- August 16, 2021